
1
Multimodal Synthetic Data Platform for Faster and Sustainable Clinical Trials
REAL CASE STUDIES
Hematological malignancies are rare and complex diseases and as a consequence, multimodal data (ranging from clinical and genomic information to images) are required to improve diagnosis, prognosis and personalized treatments.
However, collecting all these layers of information is challenging, in particular when collecting cytological and histological images from the bone marrow (BM) reproducing disease morphologic features.

2
Digital Twin and Clinical Decision Support System For Precision Medicine
REAL CASE STUDIES
Digital twin is an old term borrowed from computer science and engineering that is making new waves across healthcare, personalized medicine and drug development.
From digital twins of patients to digital twins of cells, the term is used to describe such a wide range of applications that it’s confusing at best and on the verge of becoming meaningless at worst.



1
Smart Data Query and Structuring
REAL CASE STUDIES
Optimize the search of clinical data across multiple documents within the EHR system by creating structured datasets in CDM format
2
GPT Knowledge Base & Data Retrieval
REAL CASE STUDIES
Chatbot to search for information and guidelines quickly on multiple documents within knowledge bases

3
Automatic Medical Notes
REAL CASE STUDIES
Automatically generate structured clinical notes through speech-to-text and generative AI technologies
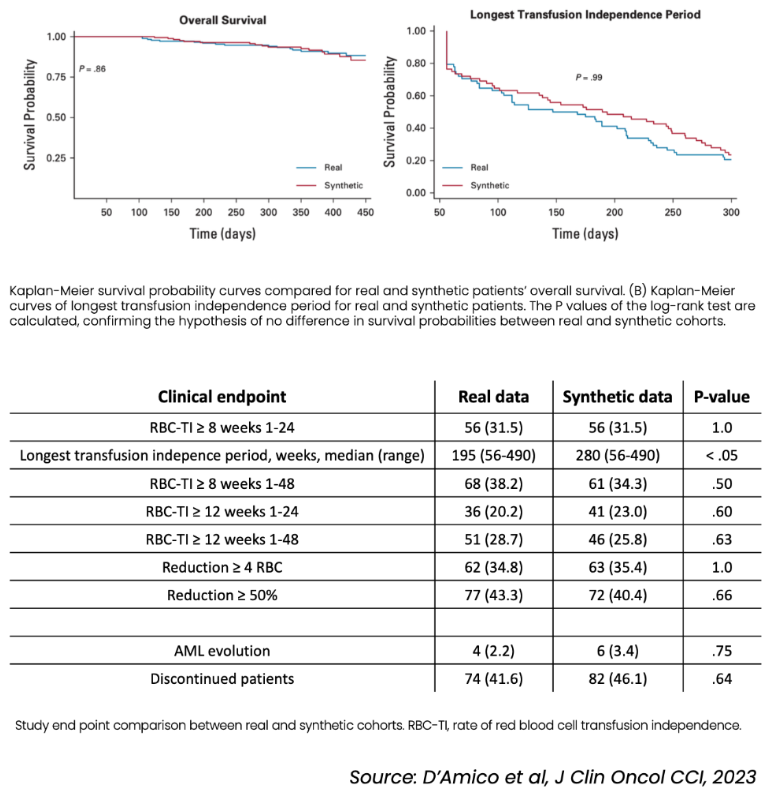
Synthetic Patients Control Arms in Luspatercept Clinical Trial for Treatment of Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS)
We investigated the possibility to use a synthetic data set as a comparison group in a clinical trial. We therefore aimed to replicate a real patient cohort from a multicenter study including 187 patients with MDS who were treated with luspatercept.
Eligible patients were:
-
Age 18 years or older
-
Had an MDS with ring sideroblasts
-
Were receiving regular red blood cells transfusions
-
Were refractory to erythropoiesis-stimulating agent therapy
Synthetic Data Generation by Artificial Intelligence in Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Applied to the Italian MS Register
To test the capability of advanced SD generation methods to replicate results of a comparative effectiveness analysis between an early initiation treatment (EIT) with high-efficacy disease-modifying therapies (HE-DMTs) and escalation strategies (ESC) on the first progression independent of relapse activity (PIRA) event risk performed on real data from the Italian MS Register (IMSR)
Our results demonstrate that:
-
The use of advanced SD generation methods may confirm and improve the results obtained by using real data.
-
An early start of HE-DMTs was confirmed to be more effective in reducing the risk of reaching a first PIRA event, by using a

